Matter will expand or contract as a result of temperature change.
WATCH THE VIDEO!
Other Demos of Interest:
 |
 |
 |
|
Work by Expanding Air |
Objects Expanding in Vacuum |
Atoms in Solids & Liquids |
Possible Incorporated Topics:
- atomic motion
- temperature change
- kinetic energy
- material properties
Theory
Matter will expand or contract as a result of a change in temperature. It can change in length, area, and volume.
Each material has a thermal expansion coefficient, which determines to what degree a material will expand/contract when undergoing a temperature change.
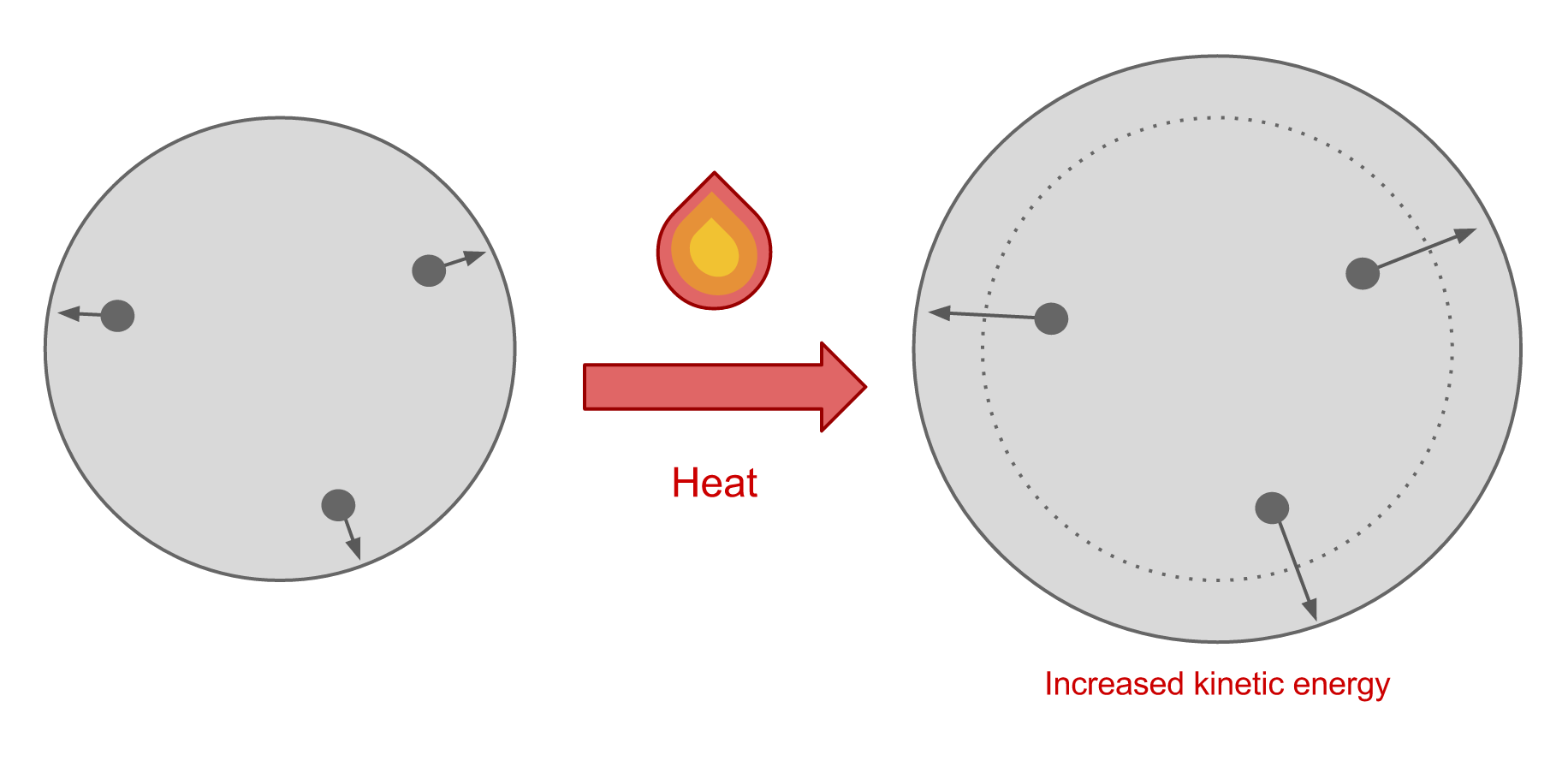
Materials tend to expand when heated and contract when cooled. This is a result of the motion of the molecules in the material. When a material is heated, energy is added to the system which increases the kinetic energy of the molecules. This causes the molecules to move faster, and as a result, they become more spread apart. This accounts for the expansion that we see.
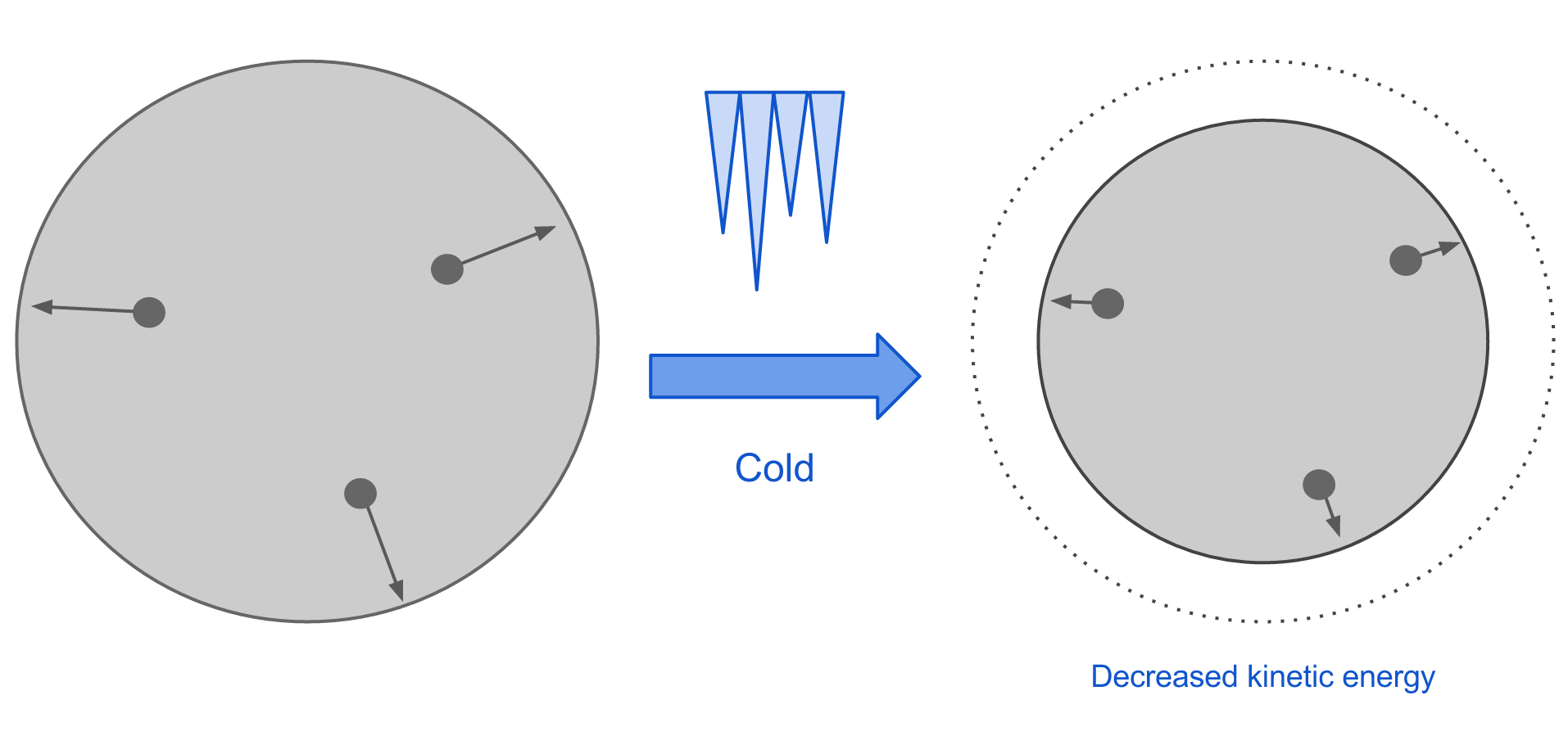
When a material is cooled, the system loses kinetic energy so the velocity of the molecules decreases. This causes them to become more closely spaced, so overall the material contracts.
Apparatus:
- metal ball and loop
- liquid nitrogen (as well as appropriate safety equipment for handling: safety glasses and cryogenic gloves)
Procedure:
- note how at room temperature, the ball fits easily through the ring
- immerse the ring in liquid nitrogen to cool it
- note how the ball no longer fits through the ring as the diameter of the ring has contracted



