Description:
Eclipses occur as a result of the geometry between the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
Watch Video:
Other Demos of Interest:
Possible Incorporated Topics:
- celestial geometry
- orbital mechanics
- angular diameter
Theory:
Eclipses occur due to the geometry of the Earth, Moon, and Sun relative to one another. There are two types of eclipses: solar eclipses and lunar eclipses.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
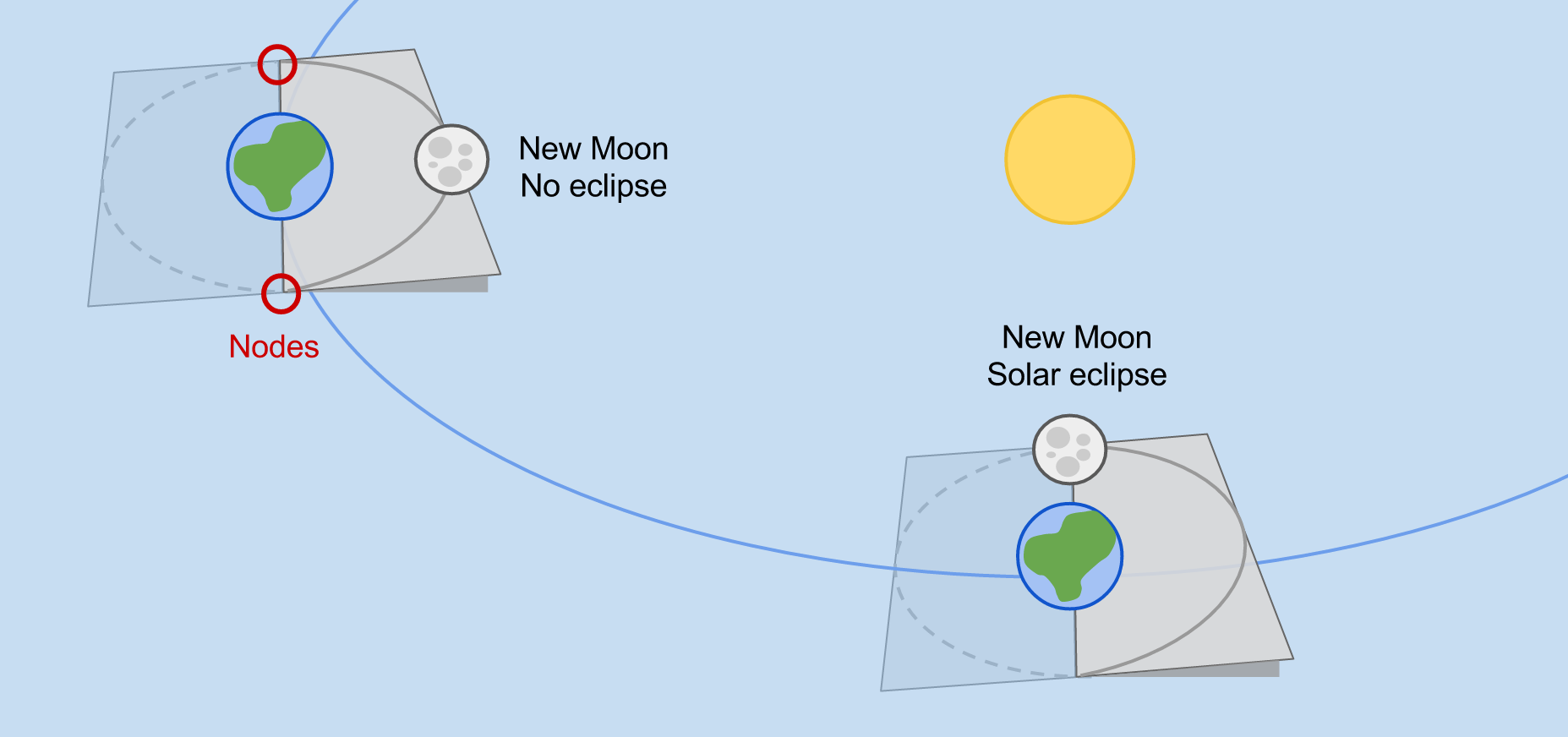
Solar eclipses can occur when the Moon passes between the Earth and Sun. This is when the phase of the Moon is New Moon.
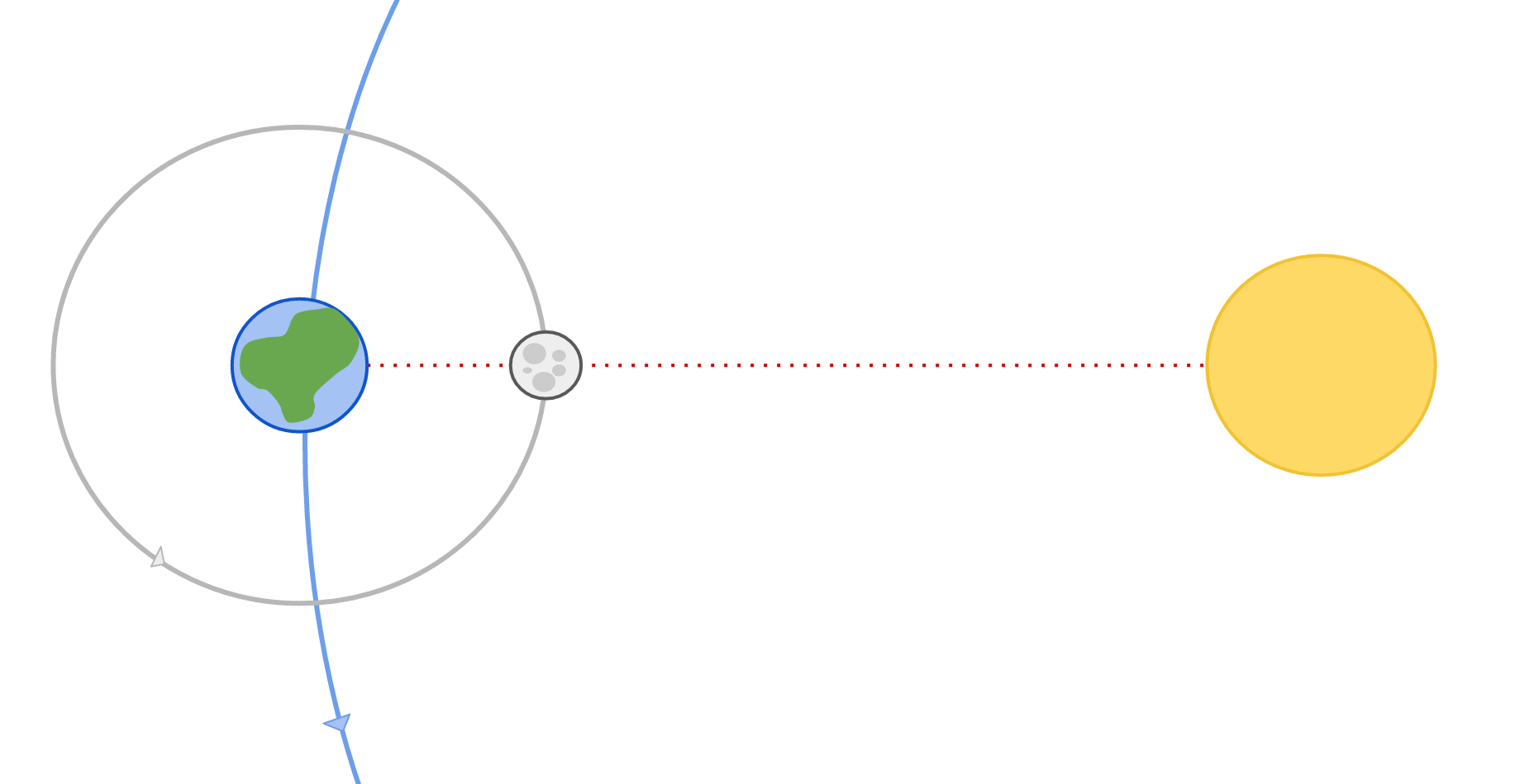
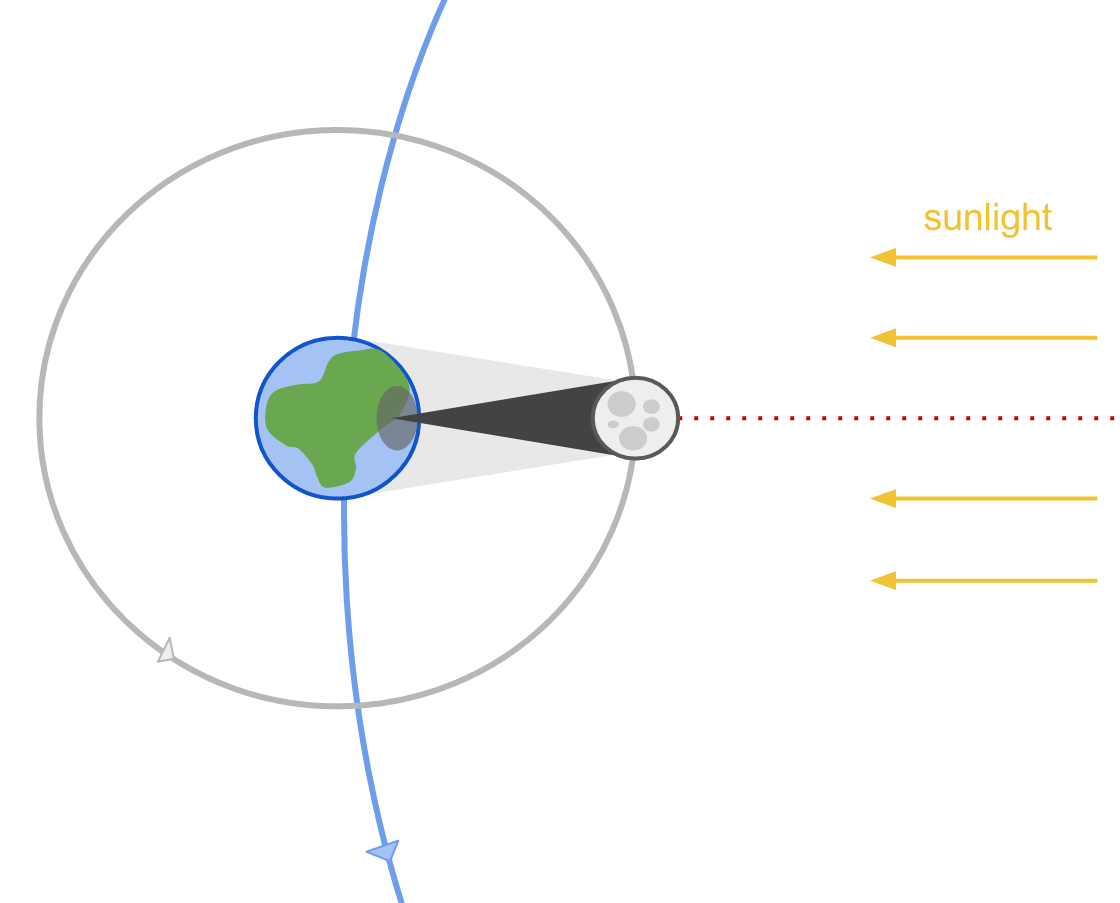
The Sun and the Moon are the same angular diameter when viewed from Earth. The Sun is ~400x bigger than the Moon, but it is also ~400x farther away from Earth than the Moon, so the two appear about the same size in the sky. Because of the this, the Moon obscures the Sun when it passes in front of it during a solar eclipse. This offers a good opportunity to study the outer atmosphere of the Sun, the corona, as the Moon covers the surface of the Sun, allowing us to see the atmosphere in detail.
A total solar eclipse will not be seen everywhere on Earth, but only along the path where the Moon’s shadow falls, the “Path of Totality”. Nearby regions can experience a partial solar eclipse.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
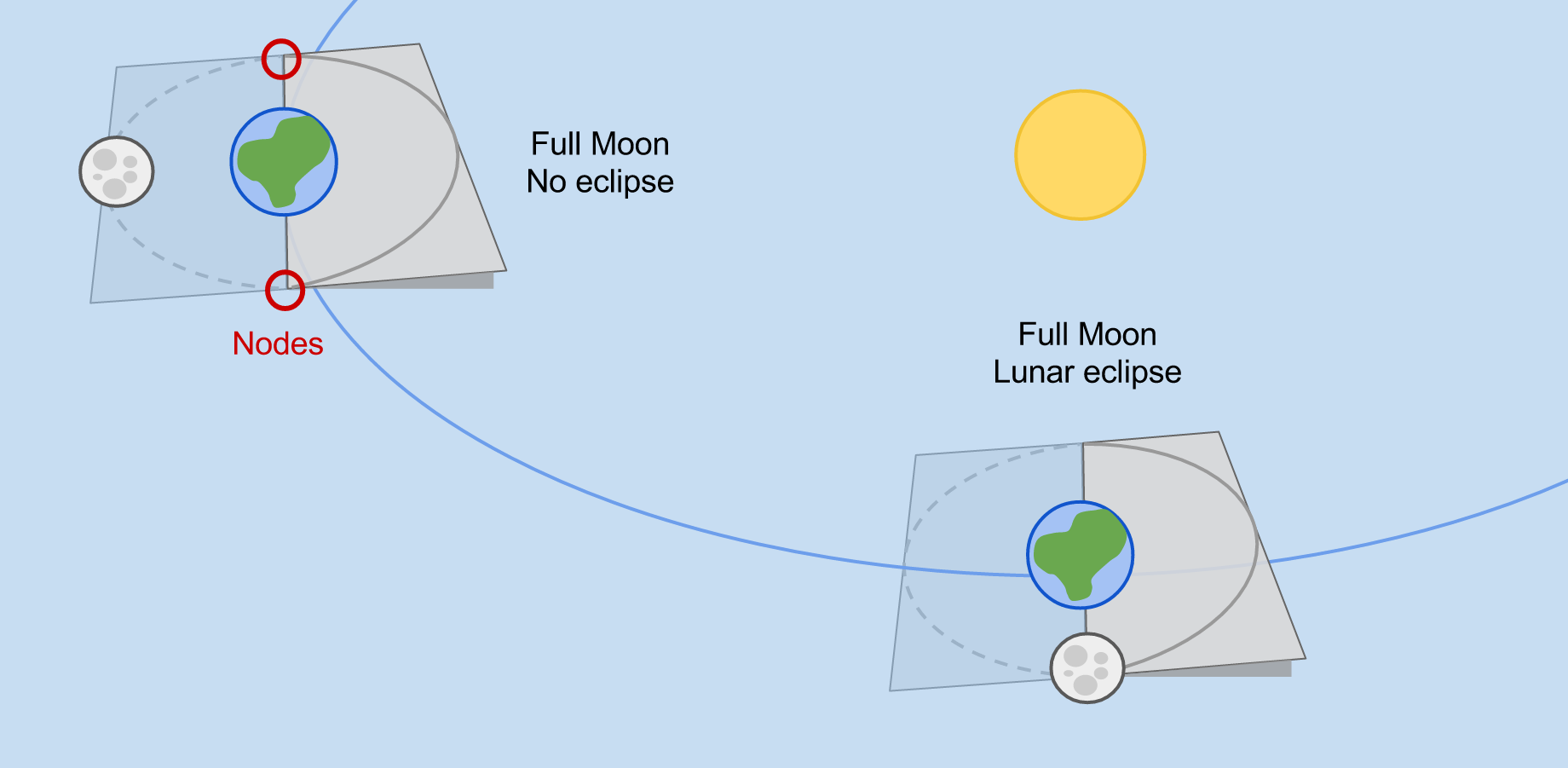
A lunar eclipse can occur when the Earth lies between the Moon and the Sun. This is when the phase of the Moon is Full Moon.
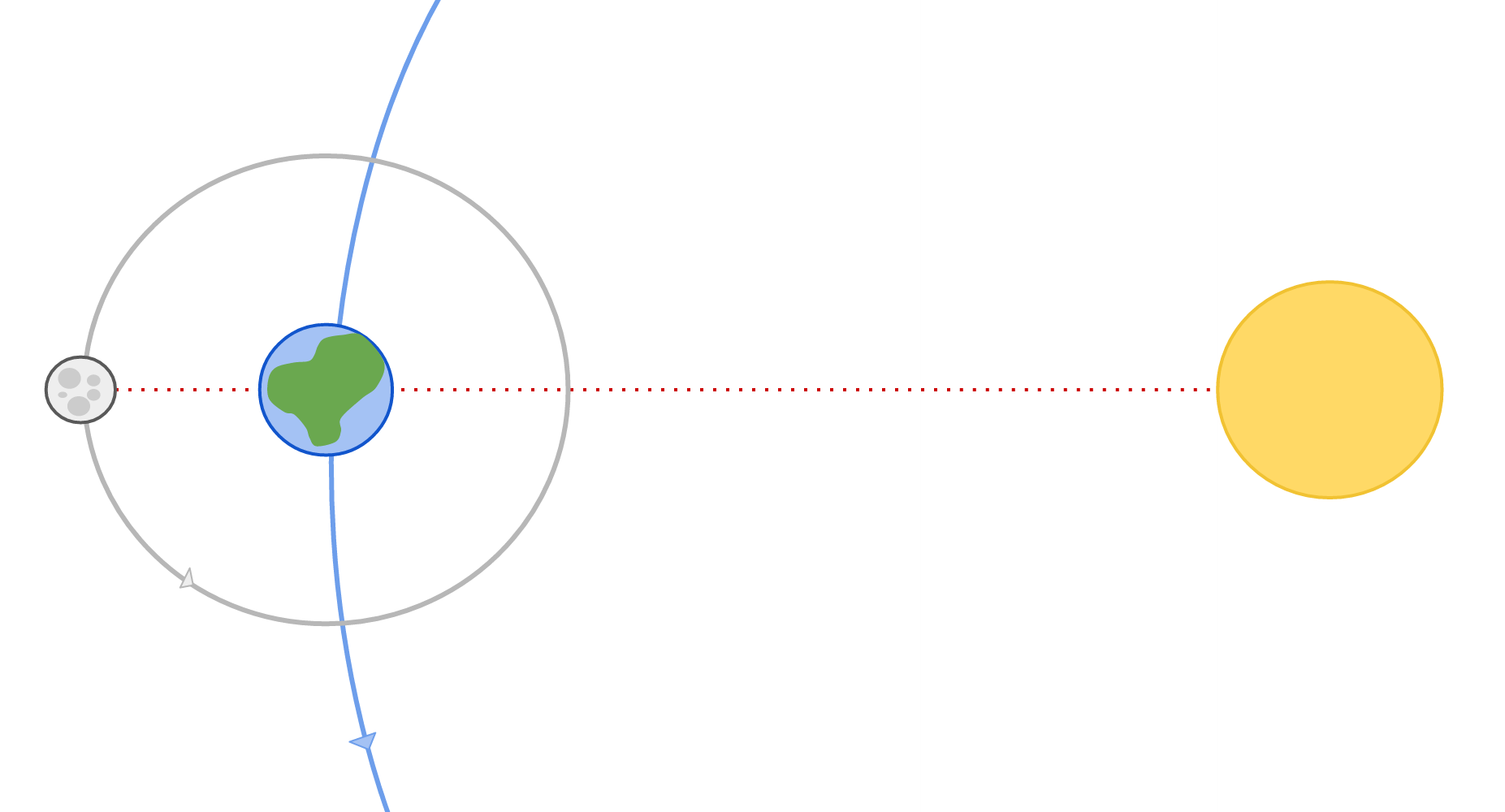
During a lunar eclipse, the Moon passes through the shadow of the Earth, obscuring it in darkness.
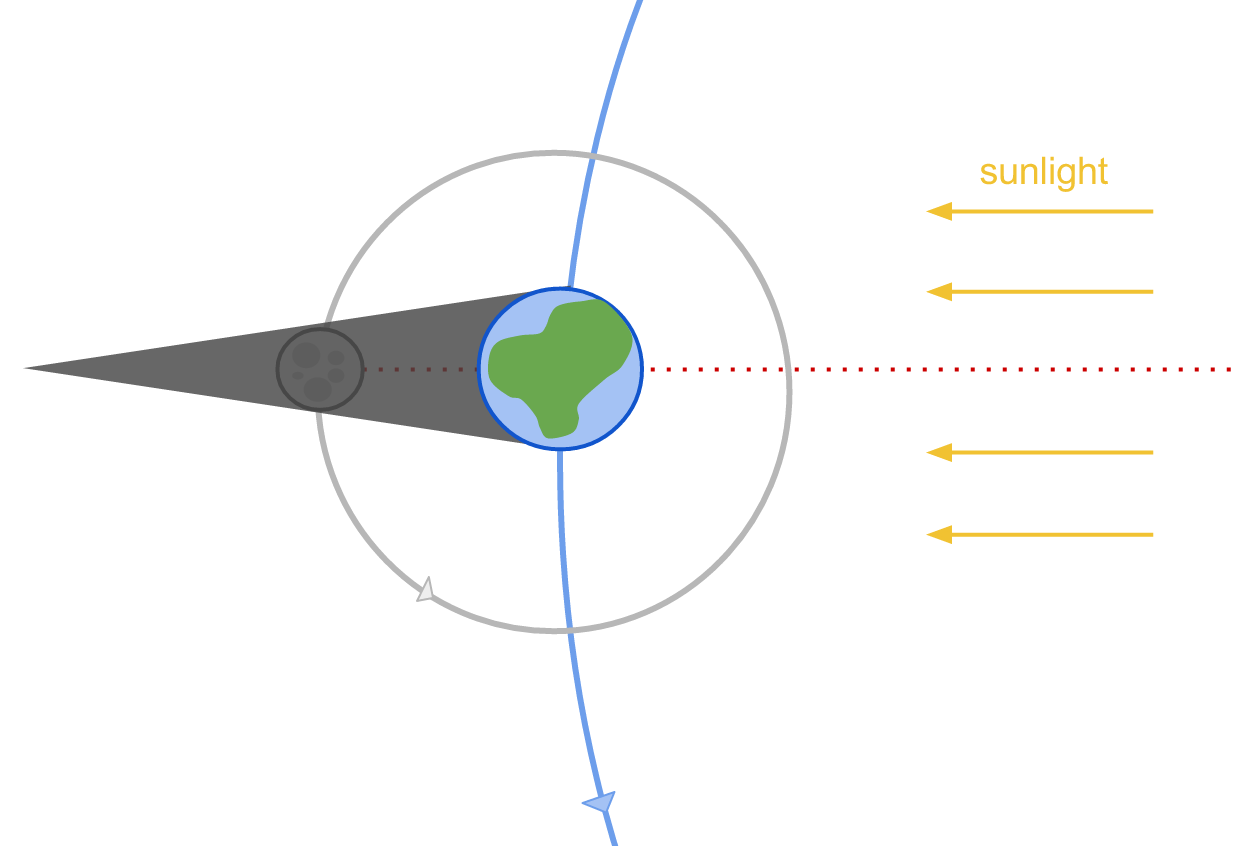
The Moon turns red during a lunar eclipse because of sunlight scattered through the Earth’s atmosphere.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Eclipses do not occur every new and full moon because the orbit of the Moon is tilted by ~5° relative to the Earth’s orbit.
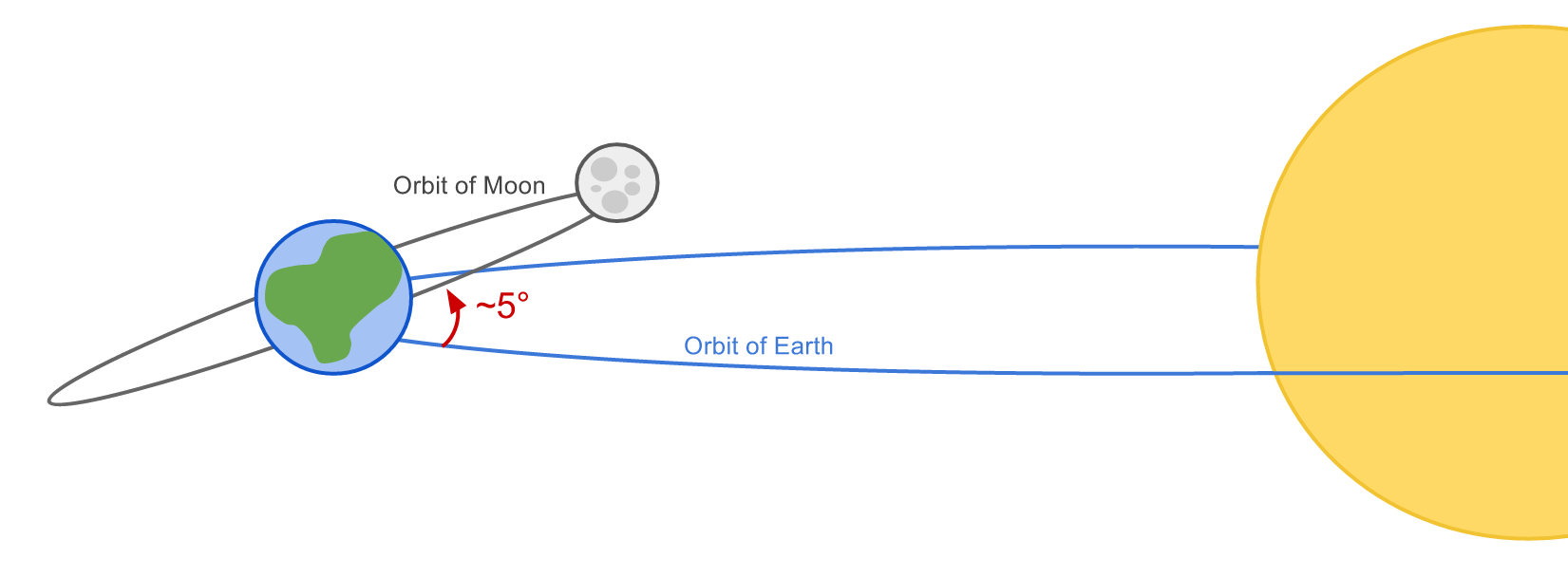
The orbits of the Moon and Earth intersect at “nodes”.
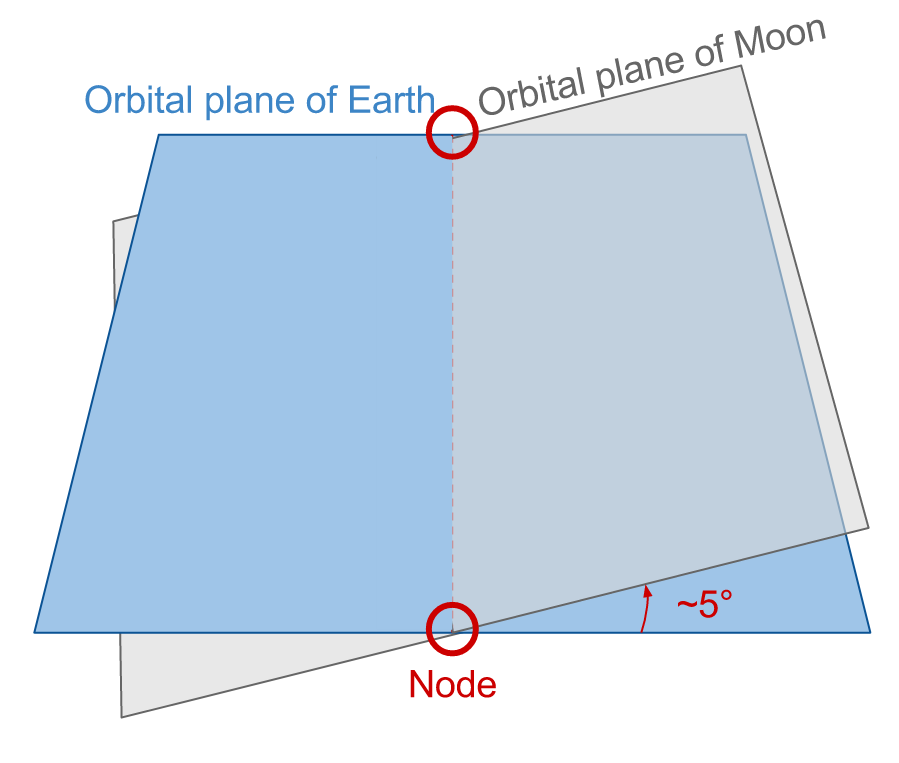
It is only when a New or Full Moon occurs at a node that we get an eclipse, as that is when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are all aligned in the same plane.
Apparatus:
- flashlight
- white balloon
- balls to represent Earth, Sun, and Moon
Procedure:
- to recreate the solar eclipse effect:
- backlight the white balloon to create the Sun
- pass the Moon ball in front of the Sun at a distance such that they have are the same size
- to recreate the lunar eclipse effect:
- shine the flashlight towards the Earth ball, and pass the Moon ball through the Earth's shadow such that it is completely obscured






